 |
|||||
| Home | Research | For Teachers | HISTORY Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
PRINCIPLES Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
CAREER Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
| Gallery | Hot Links | What's New! | |||
| Web Administration and Tools | |||||
 |
|||||
| Home | Research | For Teachers | HISTORY Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
PRINCIPLES Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
CAREER Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
| Gallery | Hot Links | What's New! | |||
| Web Administration and Tools | |||||
Aircraft Propulsion - Level 3
![]()
A turbine is any kind of spinning device that uses the action of a fluid to produce work. Typical fluids are: air, wind, water, steam and helium. Windmills and hydroelectric dams have used turbine action for decades to turn the core of an electrical generator to produce power for both industrial and residential consumption. Simpler turbines are much older, with the first known appearance dating to the time of ancient Greece.
In the history of energy conversion however, the gas turbine is relatively new. The first practical gas turbine used to generate electricity ran at Neuchatel, Switzerland in 1939, and was developed by the Brown Boveri Company. The first gas turbine powered airplane flight also took place in 1939 in Germany, using the gas turbine developed by Hans P. von Ohain. In England, the 1930's invention and development of the aircraft gas turbine by Frank Whittle resulted in a similar British flight in 1941.
The name "gas turbine'' is somewhat misleading, because to many it implies a turbine engine that uses gas as its fuel. Actually a gas turbine (as shown schematically in Fig. 1) has a compressor to draw in and compress gas (most usually air); a combustor (or burner) to add fuel to heat the compressed air; and a turbine to extract power from the hot air flow. The gas turbine is an internal combustion (IC) engine employing a continuous combustion process. This differs from the intermittent combustion occurring in Diesel and automotive IC engines.
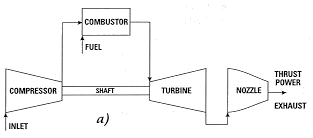
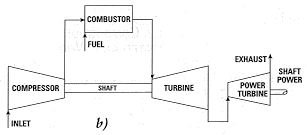
Figure 1. Schematic for a) an aircraft jet engine; and
b) a land-based gas turbine.
Because the 1939 origin of the gas turbine lies simultaneously in the electric power
field and in aviation, there have been a profusion of "other names" for the gas
turbine. For electrical power generation and marine applications it is generally called a
gas turbine, also a combustion turbine (CT), a turboshaft engine, and sometimes a gas
turbine engine. For aviation applications it is usually called a jet engine, and various
other names depending on the particular engine configuration or application, such as: jet
turbine engine; turbojet; turbofan; fanjet; and turboprop or prop jet (if it is used to
drive a propeller). The compressor-combustor-turbine part of the gas turbine (Fig. 1) is
commonly termed the gas generator.
The original article from which this section is extracted, Introduction to Gas Turbines for Non-Engineers, by Lee S. Langston, University of Connecticut and George Opdyke, Jr., Dykewood Enterprises, can be found in the ASME International Gas Turbine Institute's "Global Gas Turbine News", Volume 37, No.2, 1997, and has been used with permission.
Send all comments to ![]() aeromaster@eng.fiu.edu
aeromaster@eng.fiu.edu
© 1995-98 ALLSTAR Network. All rights reserved worldwide.
| Funded in part by | From ASME The International Gas Turbine Institute |
Updated: February 23, 1999