 |
|||||
| Home | Research | For Teachers | HISTORY Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
PRINCIPLES Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
CAREER Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
| Gallery | Hot Links | What's New! | |||
| Web Administration and Tools | |||||
 |
|||||
| Home | Research | For Teachers | HISTORY Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
PRINCIPLES Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
CAREER Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
| Gallery | Hot Links | What's New! | |||
| Web Administration and Tools | |||||
![]()
For an airplane to fly, it must always engage in a tug of war between the opposing forces of lift versus weight and thrust versus drag.
For a moment, think of an airplane moving from right to left and the flow of air moving from left to right. The weight or force due to gravity pulls down on the plane opposing the lift created by air flowing over the wing. Thrust is generated by the propeller and opposes drag caused by air resistance to the airplane. During take off, thrust must be greater than drag and lift must be greater than weight so that the airplane can become airborne.
For landing thrust must be less than drag, and lift must be less than weight.
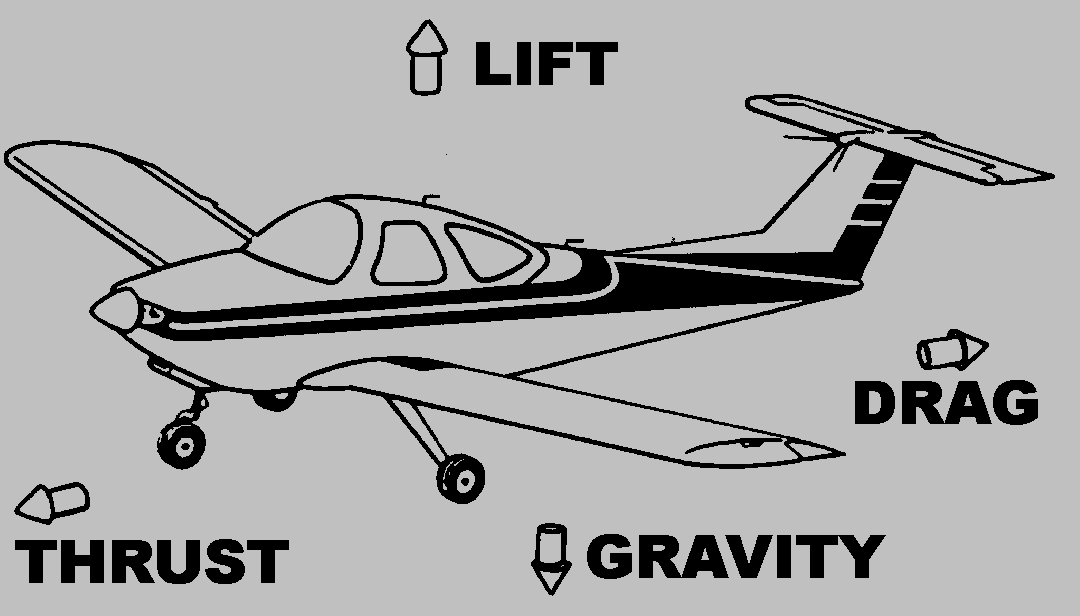
An airplane in flight is the center of a continuous tug of war between four forces: lift, gravity force or weight, thrust, and drag. Lift and Drag are considered aerodynamic forces because they exist due to the movement of the aircraft through the air. The weight pulls down on the plane opposing the lift created by air flowing over the wing. Thrust is generated by the propeller and opposes drag caused by air resistance to the frontal area of the airplane. During take off, thrust must overcome drag and lift must overcome the weight before the airplane can become airborne. In level flight at constant speed, thrust exactly equals drag and lift exactly equals the weight or gravity force. For landings thrust must be reduced below the level of drag and lift below the level of the gravity force or weight.
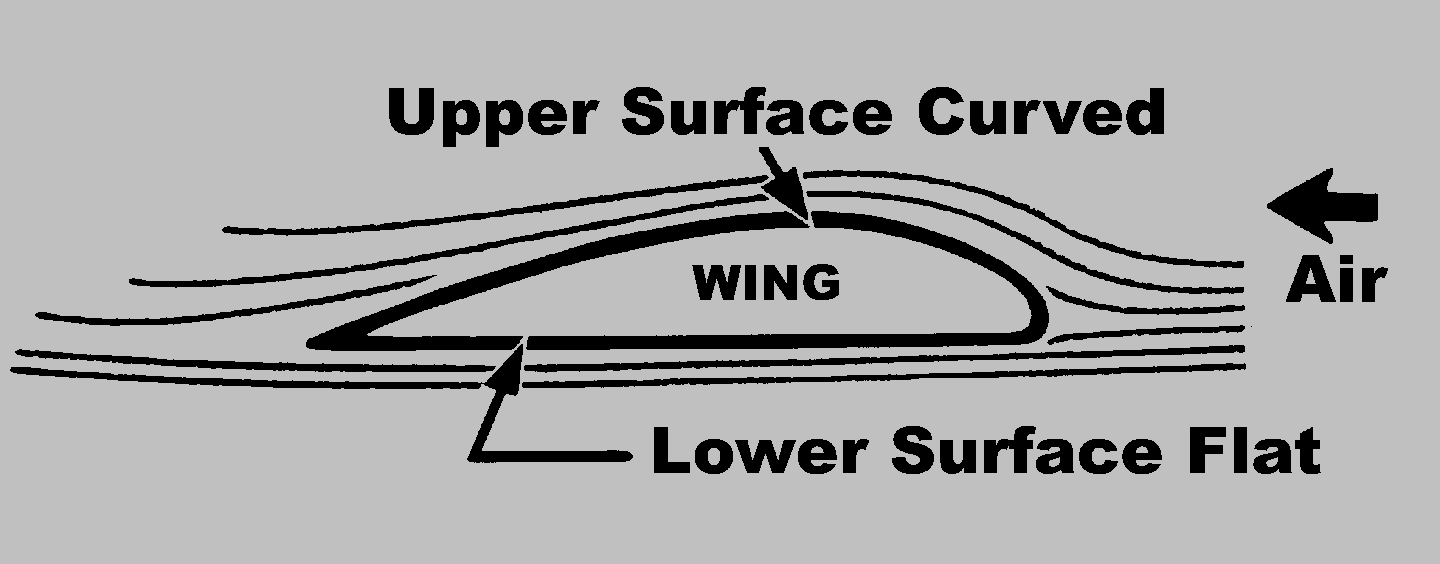
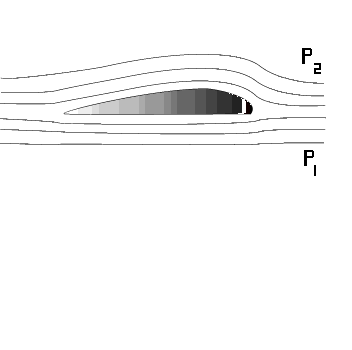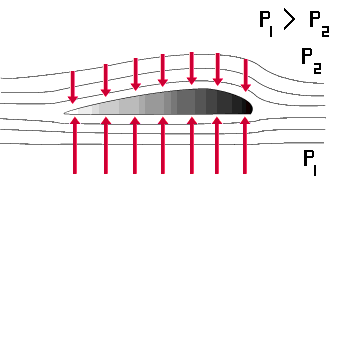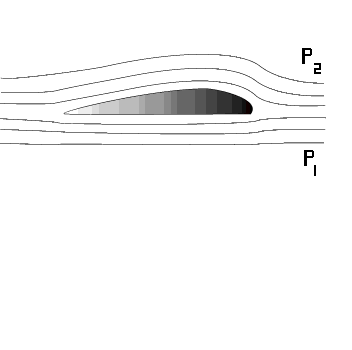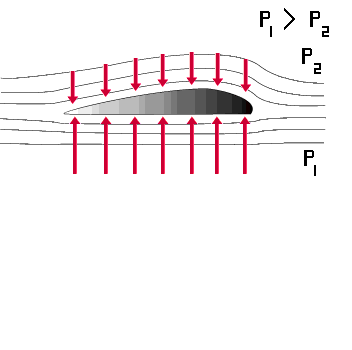
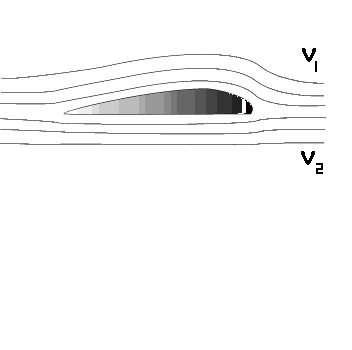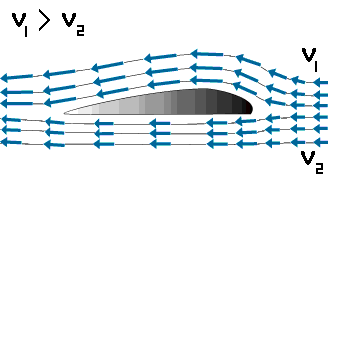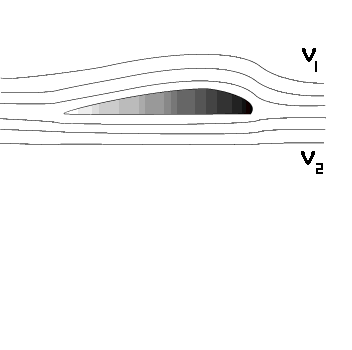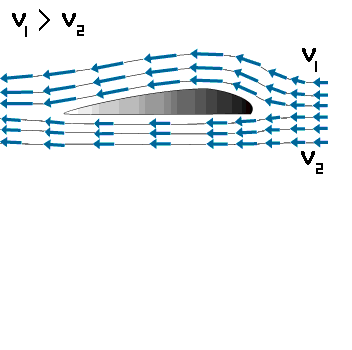
Lift is produced by a lower pressure created on the upper surface of an airplane's wing compared to the pressure on the wing's lower surface, causing the wing to be "lifted" upward. The special shape of the airplane wing (airfoil) is designed so that air flowing over it will have to travel a greater distance faster, resulting in a lower pressure area (see illustration) thus lifting the wing upward. Lift is that force which opposes the force of gravity (or weight).
 |
 |
Press ![]() to see Animation
on how lift is produced
to see Animation
on how lift is produced
Thrust is a force created by a power source which gives an airplane forward motion. It can either "pull" or "push" an airplane forward. Thrust is that force which overcomes drag. Conventional airplanes utilize engines as well as propellers to obtain thrust.
Drag is the force which delays or slows the forward movement of an airplane through the air when the airflow direction is opposite to the direction of motion of the airplane. It is the friction of the air as it meets and passes over and about an airplane and its components. The more surface area exposed to rushing air, the greater the drag. An airplane's streamlined shape helps it pass through the air more easily.
If the plane flies with a tail wind, that is, a wind whose airflow is also acting in the same direction as the direction of motion of the aircraft, the "drag" actually helps move the aircraft in the direction it wants to go. However, during takeoffs and landings, aircraft normally fly into the wind.
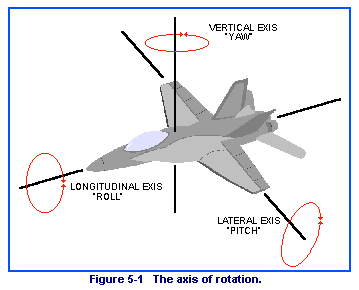
An airplane in flight changes direction by movement around one or more of its three axes of rotation: lateral axis, vertical axis, and longitudinal axis. These axes are imaginary lines that run perpendicularly to each other through the exact weight center of the airplane. The airplane's rotation around them is called pitch, roll, and yaw. The pilot guides the airplane by controlling pitch, roll, and yaw, and by use of the elevators, ailerons, and rudder.
Rudder rotates the airplane around vertical axis.
Ailerons rotate the airplane around longitudinal axis.
Elevators rotate airplane around lateral axis.
Send all comments to ![]() aeromaster@eng.fiu.edu
aeromaster@eng.fiu.edu
© 1995-98 ALLSTAR Network. All rights reserved worldwide.
Updated: February 23, 1999