 |
|||||
| Home | Research | For Teachers | HISTORY Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
PRINCIPLES Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
CAREER Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
| Gallery | Hot Links | What's New! | |||
| Web Administration and Tools | |||||
 |
|||||
| Home | Research | For Teachers | HISTORY Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
PRINCIPLES Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
CAREER Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 |
| Gallery | Hot Links | What's New! | |||
| Web Administration and Tools | |||||
![]()
Thank you ,
1. Label the parts of the aircraft shown below.
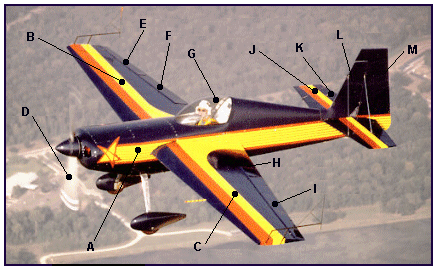
| Answer: | Answer: | ||
| A. | Fuselage | B. | Right Wing |
| C. | Left Wing | D. | Propeller |
| E. | Right Aileron | F. | Right Flap |
| G. | Cockpit | H. | Left Flap |
| I. | Left Aileron | J. | Horizontal Stabilizer |
| K. | Elevator | L. | Vertical Stabilizer |
| M. | Rudder |
2. Complete the chart of landing gear types by filling in the first column with the correct term: conventional, tricycle, or tandem. Use the description to guide you.
| Answer: | ||
| A. | Tricycle | Easiest for pilot to make a safe landing. |
| B. | Tandem | The landing gear is in two sets on the fuselage. Allows the use of highly flexible wing. |
| C. | Conventional | Most difficult for pilot to control the plane. Used in earlier aircraft; would often pitch over. |
3. Match the following statements with the BEST response. Choose the appropriate
answer from the drop down menu.
| Answer: | ||
| A. | Ribs | Structure on a wing that supports the skin and provides the airfoil shape. |
| B. | Semimonocoque | The type of fuselage where the skin and internal braces carry the flight stresses. |
| C. | Elevator | Movable section of the horizontal stabilizer that pitches nose up or down. |
| D. | Tension | Type of stress that pulls things apart. |
| E. | Vertical Stabilizer | Vertical structure that prevents an airplane from rolling over. |
| F. | Reciprocating | Movement up and down, back and forth. |
| G. | Torsion | Type of stress which is caused by twisting. |
| H. | Spars | Structure bearing the major part of the wing's load. |
| I. | Fuselage | Body of a plane that must be strong and streamlined. |
| J. | Full cantilever | Strongest type of system for attaching the wings to the fuselage. |
Send all comments to ![]() aeromaster@eng.fiu.edu
aeromaster@eng.fiu.edu
© 1995-98 ALLSTAR Network. All rights reserved worldwide.
Updated: February 23, 1999